Closures in JavaScript: A Complete Guide
JavaScript is a powerful and flexible programming language widely used for web development. One of its most fascinating and essential features is the concept of closures. If you are serious about mastering JavaScript, understanding closures is non-negotiable.
In this article, we will explore what closures are, how they work, when to use them, and provide practical examples to cement your understanding.
What is a Closure in JavaScript?
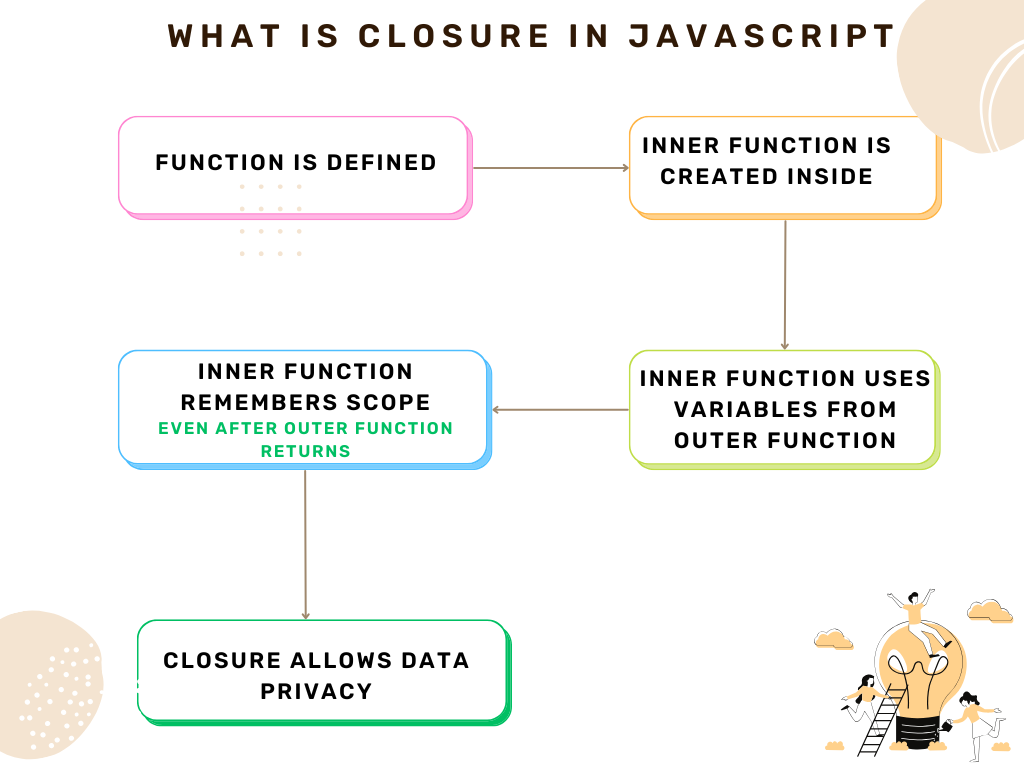
A closure is created when a function is able to remember and access its lexical scope even when it is executed outside of that scope.
In simpler terms:
A closure allows a function to access variables from an outer function even after the outer function has finished executing.
Closures give JavaScript developers the ability to create private variables, maintain state between function calls, and create more modular code.
Why are Closures Important?
Closures are essential because they:
- Preserve data between function calls
- Encapsulate logic and variables, leading to cleaner code
- Enable powerful programming patterns like currying, memoization, and module patterns
- Control variable visibility, enhancing security and maintainability
Without closures, JavaScript would be far less flexible for building modern applications.
How Closures Work: Basic Concept
When a function is created in JavaScript, it remembers the environment in which it was created. This “remembered” environment is the closure.
Here’s a simple example:
function outerFunction() {
let outerVariable = 'I am from the outer scope';
function innerFunction() {
console.log(outerVariable); // innerFunction can access outerVariable
}
return innerFunction;
}
const myClosure = outerFunction();
myClosure(); // Output: "I am from the outer scope"Explanation:
outerFunctiondefines a local variableouterVariable.innerFunctionaccessesouterVariableeven afterouterFunctionhas finished executing.myClosuremaintains a reference to the environment where it was created.
This mechanism is the closure at work!
Real-World Examples of Closures
1. Private Variables
Closures can simulate private variables — variables that cannot be accessed directly from outside the function.
function createCounter() {
let count = 0;
return {
increment() {
count++;
console.log(count);
},
decrement() {
count--;
console.log(count);
}
};
}
const counter = createCounter();
counter.increment(); // 1
counter.increment(); // 2
counter.decrement(); // 1Here, count is hidden from the outside world, only accessible through increment and decrement methods.
2. Callback Functions
Closures are heavily used in callbacks, especially in asynchronous programming (like event listeners, timers, and promises).
function greet(name) {
return function(message) {
console.log(`${message}, ${name}!`);
}
}
const greetJohn = greet('John');
greetJohn('Hello'); // Output: Hello, John!
greetJohn('Good Morning'); // Output: Good Morning, John!The returned function remembers the name variable from its creation context.
Key Points to Remember about Closures
- A closure is a combination of a function and the lexical environment within which that function was declared.
- Closures allow functions to have private data.
- Variables inside closures are preserved between executions.
- Overusing closures in large-scale applications without understanding them can lead to memory leaks.
- Always be cautious when using closures inside loops — you might capture unexpected values.
Common Mistakes and Best Practices
Mistake:
Using closures incorrectly inside loops.
for (var i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(i);
}, 1000);
}
// Output: 3 3 3Solution:
Use let instead of var, or create a new scope using an IIFE (Immediately Invoked Function Expression).
for (let i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(i);
}, 1000);
}
// Output: 0 1 2What is a closure in JavaScript with example?
Why are closures important in JavaScript?
1.Preserve data across multiple function calls
2.Create private variables and encapsulate logic
3.Build advanced features like function currying and data hiding Closures are essential for developing robust, modular, and secure JavaScript applications.
How do closures work in JavaScript?
Can closures cause memory leaks?
How can closures be used to create private variables?
What are common mistakes when using closures in JavaScript?
2.Holding unnecessary references leading to memory leaks
3.Overusing closures causing code complexity
4.Forgetting that closures keep their own private copies of variables, leading to unexpected results
Using
let instead of var in loops often solves common closure mistakes.What is the difference between closures and scope?
All closures have scopes, but not all scopes necessarily create closures.
Are closures synchronous or asynchronous in JavaScript?
setTimeout, Promises, and event listeners where they help retain access to variables at the time the async operation was set up.Conclusion
Closures are a fundamental concept in JavaScript that empowers developers to write powerful, flexible, and maintainable code. They might seem confusing at first, but with practice, closures will become one of your favorite tools.
Whether you’re building web applications, working with event handlers, or creating secure modules, mastering closures will take your JavaScript skills to the next level.