Here’s a complete blog-style article on Functions in JavaScript, covering types, syntax, keywords, and frequently asked questions (FAQs). This would work well as a blog post or educational content for learners or developers brushing up their skills.
🧠 What is a Function?
A function is a reusable block of code that performs a specific task.
function greet() {
console.log("Hello, world!");
}
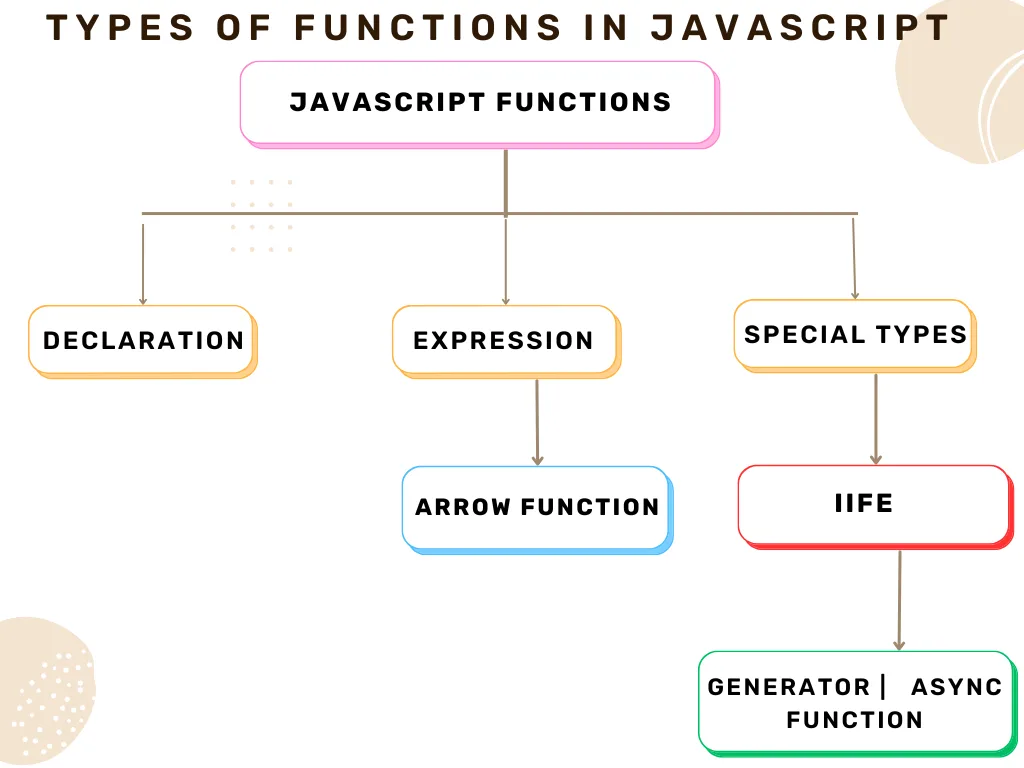
greet(); // Output: Hello, world!🧩 Types of Functions in JavaScript
JavaScript supports several ways to define functions:
1. Function Declaration
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}- Hoisted (can be called before it’s defined).
- Best for readability and reusability.
2. Function Expression
const subtract = function(a, b) {
return a - b;
};- Not hoisted.
- Can be anonymous or named.
3. Arrow Function (ES6+)
const multiply = (a, b) => a * b;- Shorter syntax.
- Does not bind
this,arguments, orsuper.
4. Immediately Invoked Function Expression (IIFE)
(function() {
console.log("I run immediately!");
})();- Used to avoid polluting the global scope.
5. Constructor Function (Rarely used directly)
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const p = new Person("Alice");- Used with the
newkeyword to create objects.
6. Generator Function
function* genFunc() {
yield 1;
yield 2;
}- Use
function*andyield. - Useful for lazy evaluation or streams.
7. Async Function
async function fetchData() {
let response = await fetch('https://api.example.com/data');
return await response.json();
}- Always returns a Promise.
- Use
awaitinside it for asynchronous code.
🛠️ Important Function Keywords
| Keyword | Description |
|---|---|
function | Declares a function |
return | Returns a value from a function |
this | Refers to the current execution context |
arguments | Array-like object containing arguments passed |
async/await | Used for asynchronous operations |
yield | Pauses and resumes generator functions |
🌍 Real-world Example
function calculateTotal(items, tax) {
return items.reduce((total, item) => total + item.price, 0) * (1 + tax);
}
const cart = [
{ name: "Book", price: 10 },
{ name: "Pen", price: 2 }
];
console.log(calculateTotal(cart, 0.1)); // 13.2
🧾 Summary
| Type | Arrow Support | this Behavior | Hoisted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function Declaration | ❌ | Bound | ✅ |
| Function Expression | ✅ | Lexical (this) | ❌ |
| Arrow Function | ✅ | Lexical | ❌ |
| IIFE | ✅ | As defined | ❌ |
| Generator Function | ❌ | Bound | ✅ |
| Async Function | ✅ | Bound | ✅ |
What is the difference between function declaration and expression?
Declaration is hoisted.
Expression is not hoisted and can be anonymous.
Expression is not hoisted and can be anonymous.
Why use arrow functions?
Short syntax.
Useful when you don’t want a new
Useful when you don’t want a new
this context.Can functions return other functions?
Yes! Functions are first-class citizens.
function outer(x) {
return function inner(y) {
return x + y;
};
}
console.log(outer(5)(3)); // 8
function outer(x) {
return function inner(y) {
return x + y;
};
}
console.log(outer(5)(3)); // 8
What’s the arguments object?
A special object available in regular functions, containing passed arguments.
function showArgs() {
console.log(arguments);
}
showArgs(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
function showArgs() {
console.log(arguments);
}
showArgs(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
📌 Final Thoughts
Functions in JavaScript are powerful tools — mastering them will improve your coding skills, from simple scripts to scalable applications. Keep experimenting with different types and use cases to understand which one fits your needs.