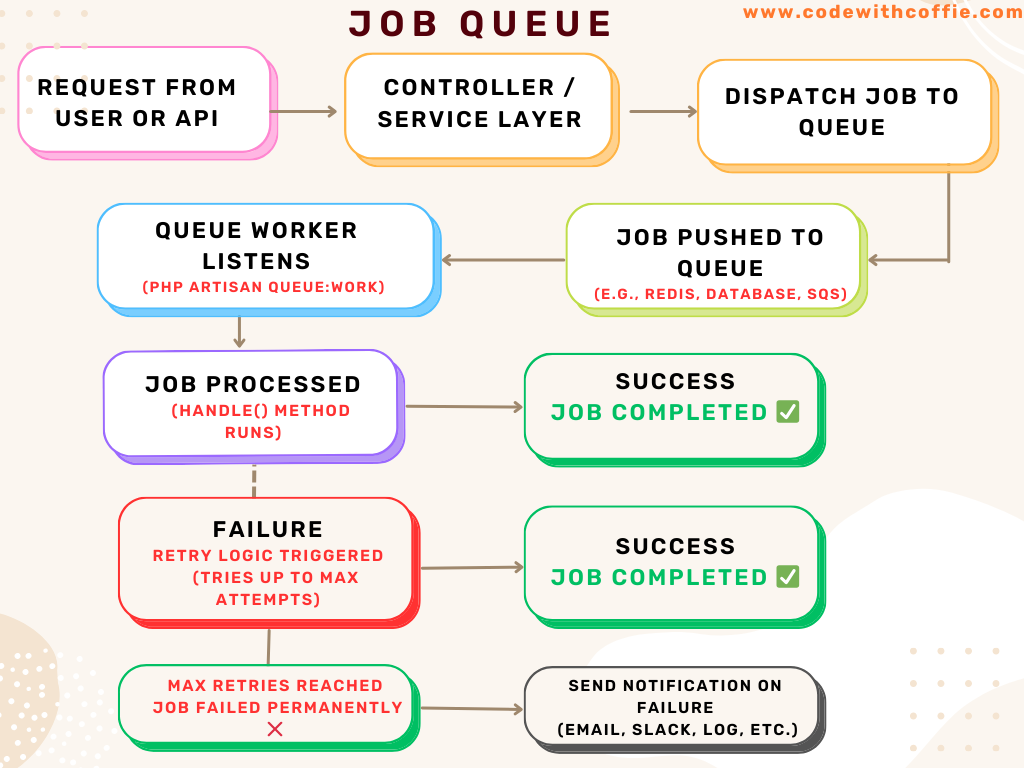
What is a Job Queue in Laravel?
Laravel Job Queue is a powerful feature that allows you to defer time-consuming tasks to be processed in the background. This ensures that your application responds to users quickly, offloading heavy tasks like email sending, report generation, video processing, or third-party API calls to a queue worker.
Laravel queues provide asynchronous processing, scalability, and performance optimization, making your application efficient and responsive even under high load.
Key Benefits of Laravel Job Queues
- ✅ Improved Performance: Tasks are executed in the background without blocking user requests.
- ✅ Scalability: Handles a high volume of tasks asynchronously.
- ✅ Reliability: Failed jobs can be retried or logged for debugging.
- ✅ Flexibility: Supports multiple queue backends like Redis, Database, Amazon SQS, and more.
- ✅ Control & Monitoring: Easily monitor and manage jobs with Laravel Horizon.
Supported Queue Drivers in Laravel
Laravel supports various queue backends:
| Driver | Description |
|---|---|
| Database | Stores jobs in the database (good for beginners) |
| Redis | Fast, in-memory job storage (ideal for scaling) |
| Amazon SQS | Scalable AWS managed queue |
| Beanstalkd | Simple work queue |
| Synchronous | Processes job immediately (for testing only) |
| Null | Discards jobs (used for disabling queues) |
You can configure the queue driver in .env:
QUEUE_CONNECTION=databaseStep-by-Step: How to Use Job Queue in Laravel
1. Setup Database Queue (Example)
Generate the migration:
php artisan queue:table
php artisan migrate2. Create a Job Class
Create a job using Artisan:
php artisan make:job SendWelcomeEmailThe job will be created in app/Jobs/SendWelcomeEmail.php:
public function handle()
{
Mail::to($this->user)->send(new WelcomeEmail($this->user));
}3. Dispatch a Job
You can dispatch jobs using:
WelcomeEmail::dispatch($user);With a delay:
SendWelcomeEmail::dispatch($user)->delay(now()->addMinutes(5));To a specific queue:
SendWelcomeEmail::dispatch($user)->onQueue('emails');4. Process Jobs with Queue Worker
Start processing jobs:
php artisan queue:workContinuous background processing:
php artisan queue:work --daemonProcess specific queues:
php artisan queue:work --queue=emails,defaultManaging Failed Jobs
Create failed jobs table:
php artisan queue:failed-table
php artisan migrateView failed jobs:
php artisan queue:failedRetry failed jobs:
php artisan queue:retry {job_id}Queue Prioritization
Laravel allows assigning priorities by using different queues. Workers can be instructed to process high-priority queues first:
php artisan queue:work --queue=high,default,lowQueue Middleware (Advanced Control)
You can add middleware to jobs for rate limiting, preventing overlaps, etc. Example:
phpCopyEditpublic function middleware()
{
return [new WithoutOverlapping($this->userId)];
}Queue Monitoring with Laravel Horizon
If using Redis, Laravel Horizon provides a real-time dashboard to monitor jobs, failed jobs, throughput, and more.
Install Horizon:
bashCopyEditcomposer require laravel/horizon
php artisan horizon:install
php artisan migrateStart Horizon:
php artisan horizonAccess dashboard at:
http://your-app.com/horizonQueue Optimization Tips
- Use Redis for performance and scalability.
- Use Supervisor or systemd to keep queue workers running.
- Use batch processing for handling multiple jobs.
- Use job throttling and rate limiting for APIs.
- Regularly monitor and retry failed jobs.
- Use queues for tasks like emails, notifications, video processing, imports/exports.
Queue vs Scheduled Tasks
| Queue Jobs | Scheduled Tasks |
|---|---|
| Event-driven (triggered by user/event) | Time-driven (runs at scheduled intervals) |
| E.g., Send email after user registers | E.g., Daily report generation |
Real-World Use Cases for Laravel Queues
- Sending bulk emails
- SMS notifications
- Generating PDFs or reports
- Processing payments
- Video encoding
- Image optimization
- Import/export of large data files
- API interaction throttling
Conclusion
Laravel queues empower developers to build high-performance, scalable, and user-friendly applications by processing heavy tasks in the background. Whether you’re working on a small app or a large-scale system, mastering Laravel’s queue system is crucial for efficiency and scalability.
SEO Summary Snippet (Meta Description):
Learn how to use Laravel Job Queues for asynchronous processing. Improve app performance by offloading heavy tasks like emails, uploads, and API calls to background workers. Step-by-step guide with examples, Redis, Horizon, and queue optimization tips.
Let me know if you want this in Markdown, HTML, or need a section expanded (e.g., Horizon, Supervisor, Redis setup).